Few of PHP FAQs that you could find helpful and handy at times.
Question : Who is the father of PHP and Explain the changes in PHP Versions ?
Ans :
Rasmus Lerdorf is the father of PHP.
Versions of PHP :
- PHP 1: Released in 1995. Officially called Personal Home Page.
- PHP 3: Andi & Zeev rewrote base for this version.
- PHP 4: By Zend in 2000.
- PHP 5: In 2004 by Zend with OOPs model.
- PHP 5.3: In 2009
- PHP 5.5: in 2013
- PHP 7: in 2015
Question : Is PHP Compiled Language ? Justify your answer.
Ans :
As a general purpose programming language, PHP code is processed by an interpreter application in command-line mode performing desired operating system operatinos and producing program output on its standard output channel. If there is any syntax error in script, generally. compiling language such as a C throws and error without exeecuting single line of code and total processing takes place in two steps such as compilation and execution where as PHP executes the lnes of code till the line where there is syntax error and then throws the error when control reahes to the line of code having error. Thus, it actually interprets (indirectly executes) the code line by line.
Question : What is the name of PHP configuration file ? List any variable(s) from it.
Ans :
php . ini
register_global, max_execution_time, script_time_out, errors etc.
Question : What is difference between PHP 4 and PHP 5 ?
Ans :
- The new OOP features in PHP 5.
- In PHP 4, everything was passed b value, including objects. This has changed in PHP 5, now all objects are passed by reference.
- Unified Constructors and Destructors - PHP 5 introduces a new unified constrctor / destructors names.
In PHP 4, a constructor was simply a method that had the same name as the class itself. This caused some headaches since if you changed the name of the class, you would have to go through and change every occurence of that name.
In PHP 5, all constructors are named __construct. That is, the word construct prefixed by two underscores. Other than this name change, constructors works the same way.
Also, the newly added __destruct allows you to write code that will be executed when the object is destroyed.
- Abstract classes, Interaces.
- Some magic methods to take note of are __call, __get, __set and __toString.
- PHP 5 introduces limited type hinting. This means you can enforce what kind of variables are passed to functions or class methods.
- New extensions are added e.g. SimpleXML, DOM, XSL, PDO, HASH etc.
Question : Suppose I am writing a script where I am uploading 100 MB of file but somehow my script is giving the error, what will be the remedy or what will you do ?
Ans :
Set the upload file limit / max upload file to 100 MB or set max post size to 100 MB or set script time out at some max time.
Question : What is the difference between ECHO and PRINT command ?
Ans :
- PRINT behaves as a function whereas ECHO is not a function.
- PRINT returns TRUE or FALSE but ECHO does not.
- ECHO is faster than PRINT.
- ECHO can take multiple parameters whereas PRINT takes only one.
Question : Through which function(s) can we increase the execution time of a PHP Script ?
Ans :
Using set_time_limit ( )
We can also change the settings in php . ini file in variable named max_execution_time.
Question : What are the different types of errors that PHP supports ?
Ans :
- Notices: These are trivial, non-critical errors that PHP encounters while executing a script - e.g. accessing a variable that has not yet beeen defined. By default, such errors are not displayed to the user at all - although you can change this default behavior.
- Warnings: These are more serious errors - e.g. attempting to include() a file which does not exists. By default, these errors are displayed to the user, but they do not result in script termination.
- Fatal Errors: These are critical errors - e.g. instantiating an object of a non-existent class or calling non-existent function. These errors cause the immediate termination of the script and PHP's default behavior is to display them to the user when they take place.
- Parse Errors: When we make mistake in PHP code like, missing semicolon or any un-expected symbol in code. These errors too cause the immediate termination of the script.
Question : What is Environment Variable ?
Ans :
Enviornment, GET, POST, Cookie, Server, PHP_SELF etc.
Question : What are the differences between GET and POST methods in Form Submitting ?
Ans :
GET - GET requests a representation of specified resource. GET request can be cached. It has length restrictions. Data is passed through query string on to server, so might not always be safe. Should be used only to retrieve data. Max URL length should be 2048 characters.
POST - Submits data to be processed to a specified resource. It is never cached and can't be bookmarked where as GET can. POST has no data limitation on posting. Data is sent in HTTP message body of POST request so posted data is not visible to naked eye.
USAGE:
GET - can be used to redirect users but not posting data to server.
POST - can be used in anycase, e.g. sending sensitive info etc.
Question : How to fetch the IP Address of client machine / browser ?
Ans :
$_SERVER["remote_addr"]
Question : What are the differences between require(), require_once(), include() and include_once()?
Ans :
include() and require() are the functions which includes the file during the execution of the script. However, if file, to be included, is not found include() gives just a warning and continue execution from the next line whereas, require() gives a fatal error and stops execution of script.
include_once() and require_once() are the functions same as that of include() and require(). However, if file, to be included, is already included up above in script, then it does not produce any error but does not include that file again.
Question : What is the exit() function used for ?
Ans :
exit() terminates execution of script OR it exits the loop.
Question : How can we know the number of elements in an array ?
Ans :
With the help of functions i.e. sizeof() OR count()
Question : Using which function can we know whether a session is started or not ?
Ans :
session_is_registered() function
Question : Which is the PHP function(s) to get a row from the MySQL database ? Which is more efficient way ?
Ans :
mysql_fetch_array() OR mysql_fetch_row() OR mysql_fetch_object()
mysql_fetch_array() is more efficient than others.
Question : What is the use of mysql_insert_id() function ?
Ans :
It is used to get the Primary key ID generated from the last or previous insert operation / query.
Question : How to split a string into an array ?
Ans :
With the help of function explode().
Question : How to get an array into a string ?
Ans :
With the help of function implode().
Question : What are the parameters of mysql_connect() ?
Ans :
mysql_connect(server name, user name, password)
Question : Explain any 5 array methods ?
Ans :
- sort() : Sorts an array. This function assigns new keys to the elements in array. It will remove any existing keys that may have been assigned, rather than just re-ordering the keys.
- rsort() : Sorts an array in reverse order. This function assigns new keys to the elements in array. It will remove any existing keys that may have been assigned, rather than that just re-ordering the keys.
- asort : Sorts an array and maintain index association.
- arsort() : Sorts an array in reverse order and maintain index association.
- ksort() : Sorts an array by key.
- krsort() : Sorts an array by key in reverse order.
- count() : Counts elements in an array or properties in an object.
- usort() : Sorts an array by values using a user-defined comparison function. It can do multi-dimensional sorting but it involves building a callback function and may often pretty long-winded.
Question : Which PHP function gives you the number of rows from the result set of MySQL query ?
Ans :
mysql_num_rows() function
Question : How you will achieve "23 Mar 10" date format with mktime() ?
Ans :
mktime(hour, minute, second, month, day, year) gets Unix Timestamp for a date. This timestamp is a long integer containing the number of seconds between the Unix Epoch (January 1 1970 00:00:00 GMT) and the time specified in function.
Using date() function along with mktime will return needed format.
e.g. date("j M y", mktime(0, 0, 0, 3, 23, 2010)) for printing "23 Mar 10"
Question : How you will check "last updated date-time" of the file ?
Ans :
filetime function returns the time as a Unix timestamp, when the data blocks of a file were being written to, i.e. the time when the content of the file was changed.
Question : If I open file with "a" mode for writing task then what will happen to existing content ?
Ans :
File will get opened in append mode i.e. for writing mode only. Existing content will remain same and pointer will be placed at the end of the file being written.
- "r" : Opens file for reading only. Places the file pointer at the beginning of the file.
- "r+" : Open for reading and writing. Places the file pointer at the beginning of the file.
- "w" : Open for writing only. Places the file pointer at the beginning of the file and truncate the file to zero length. If the file does not exist, attempts to create it.
- "w+" : Open for reading and writing. Places the file pointer at the beginning of the file and truncate the file to zero length. If the file does not exist, attempts to create it.
- "a" : Open for writing only. Places the file pointer at the end of the file. If the file does not exist, attempts to create it.
- "a+" : Open for reading and writing. Places the file pointer at the end of the file. If the file does not exist, attempts to create it.
Question : How you will check the file size while file upload ?
Ans :
The global $_FILES array will contain all the uploaded file information.
- $_FILES['userfile]['name'] - The original name of the file on the client machine.
- $_FILES['userfile]['type'] - The mime type of the file, if the browser provided this information. An example would be "image/gif". This mime type is however not checked on the PHP side and therefore don't take its value for granted.
- $_FILES['userfile]['size'] - The size, in bytes, of the uploaded files.
- $_FILES['userfile]['tmp_name'] - The temporary filename of the file in which the uploaded file was stored on server.
- $_FILES['userfile]['error'] - The error code associated with this file upload. This element was added in PHP 4.2.0
'userfile' in above example is field name used on form for uploading file.
If question means check file size before uploading then its not possible with php. You'd have to get JAVASCRIPT to do it since it would be client-side before uploading. PHP is executed on the server, so it has no rights to access files on the client machine.
Question : How you will check the height and width of the image file while uploading ?
Ans :
If question means check file size before uploading then its not possible with PHP. You'd have to get JAVASCRIPT to do it since it would be client-side before uploading. PHP is executed on the server, so it has no rights to access files on the client machine.
On server side, getimagesize() function can be used to determine the dimensions. This function does not use gd library but GD library functions can be used to resize the image in required dimensions without loosing quality.
Question : How you will run shell command from PHP ?
Ans :
Using shell_exec function. It executes commands via shell and return the complete output as a string. One can also use system() function to execute commands through PHP.
Question : How can we submit a form without a submit button ?
Ans :
Using JS i.e. document . form . submit ( )
Question : In how many ways can we retrieve the date in the result set of mysql using PHP ?
Ans :
MySQL stores dates in YYYY-MM-DD format so,
date("F d, Y", strtotime($myrow['date'])); will give July 05, 2013 and
date("l, F d, Y", strtotime($myrow['date'])); will give Friday, July 05, 2013
Question : What is the difference between mysql_fetch_object and mysql_fetch_array ?
Ans :
mysql_fetch_object as name suggests, retrieves records in object format. So, usage will be,
$row = mysql_fetch_object($result);
echo $row->user_id;
mysql_fetch_array as name suggests, retrieves records in array format. Either in numeric array format or associative array format or both formats.
The only difference is, in _fetch_object, data must be accessed by field names whereas _fetch_array allows to access data by numerical offset.
Question : What is the difference between $message and $$message ?
Ans :
$message is normal variable in PHP whereas $$message is value at $message. It means, value of $message will be treated as variable and value of that evaluated variable will be given by $$message.
Question : How can we extract string 'abc.com' from a string 'http://info@abc.com' using regular expressions in PHP ?
Ans :
preg_match is our way to find substring but since it will be slow compairing to other so its not suggested. Instead either strstr or strpos should be used. So, strstr($email, '@') will give domain i.e. @abc.com or use explode($email, 'a') which will give abc.com
But since its mentioned to use regular expression so, preg_match("/abc.com/i", $email). Here, i is used for case insensitivity.
Question : How can we create a database using PHP and MySQL ?
Ans :
$conn = mysqli_connect(server, user, password);
$sql = "CREATE database test_db";
$retval = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
Note, mysql_* functions are deprecated in newer PHP versios & instead mysqli_* is introduced. MySQL is old database driver and MySQLi is improved driver, hence mysqli.
It provides,
- Object Oriented Interface
- Support for prepared statements
- Support for multiple statements
- Support for Transactions
- Enhanced debugging capability
- Embeded server support
Question : Functions in IMAP, POP3 and LDAP ?
Ans :
IMAP : Internet Message Access Protocol
- imagep_append : Appends a string message to specified mailbox.
- imap_body : Reads the message body.
- imap_close : Closes an IMAP stream.
- imap_delete : Marks a message for deletion from mailbox.
- imap_createmailbox : Creats a new IMAP mailbox.
POP3 : Post Office Protocol Version 3
Eventually, for basic POP3 access, major IMAP functions can be used.
- imap_open : Opens a specified mailbox.
- imap_fetch_overview : Fetches an overview of mailboxes.
- imap_fetchheader : Fetches a header of mail.
SMTP : Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
With a little tweaks, one can convert the sending mail via SMTP. One should change the server to SMTP server and is ready to go. Along with server, you may need to set the host, username and password (and maybe the port if it is not the default one - 25).
- mail : Sends an email.
NNTP : Network News Transfer Protocol
MIME : Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension
LDAP : Light weight Directory Access Protocol
- ldap_connect : This will connect to the ldap server with the given login credentials.
- ldap_search : By using this command we can search in ldap records.
Question : How can I execute a PHP script using command line ?
Ans :
There are three different ways :
- Tell PHP to execute a certain file.
$ php my_script.php
$ php -f my_script.php
Both ways (whether using the -f switch or not) execute the file my_script.php. Note that there is no restriction on which files can be executed; in particular, the filename is not required have a .php extension. If arguments need to be passed to the script when using -f , the first argument must be --.
- Pass the PHP code to execute directly on the command line.
$ php -r 'print_r(get_defined_constants());'
Read the example carefully: there are no beginning or ending tags! The -r switch simply does not need them, and using them will lead to a parse error.
- Provide the PHP code to execute via standard input (stdin).
$ some_application | some_filter | php | sort -u > final_output.txt
This gives the powerful ability to create PHP code dynamically and feed it to the binary, as shown in above (fictional) example.
Question : What is meant by nl2br() ?
Ans :
The nl2br() function is used to insert HTML line breaks ('<br />') before all newlines (\n) in a string. It returns the altered string.
Question : Draw the architecture of Zend Engine ?
Ans :
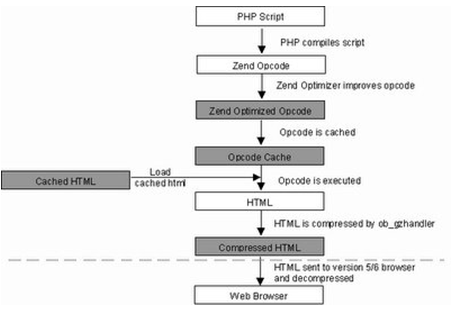
Question : What are the differences between Procedure Oriented Programming (POP) & Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
Ans :
Difference Between Procedure Oriented Programming (POP) & Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
| |
Procedure Oriented Programming |
Object Oriented Programming |
| Divided Into |
In POP, program is divided into small parts called functions. |
In OOP, program is divided into parts called objects. |
| Importance |
In POP,Importance is not given to data but to functions as well as sequence of actions to be done. |
In OOP, Importance is given to the data rather than procedures or functions because it works as a real world. |
| Approach |
POP follows Top Down approach. |
OOP follows Bottom Up approach. |
| Access Specifiers |
POP does not have any access specifier. |
OOP has access specifiers named Public, Private, Protected, etc. |
| Data Moving |
In POP, Data can move freely from function to function in the system. |
In OOP, objects can move and communicate with each other through member functions. |
| Expansion |
To add new data and function in POP is not so easy. |
OOP provides an easy way to add new data and function. |
| Data Access |
In POP, Most function uses Global data for sharing that can be accessed freely from function to function in the system. |
In OOP, data can not move easily from function to function,it can be kept public or private so we can control the access of data. |
| Data Hiding |
POP does not have any proper way for hiding data so it is less secure. |
OOP provides Data Hiding so provides more security. |
| Overloading |
In POP, Overloading is not possible. |
In OOP, overloading is possible in the form of Function Overloading and Operator Overloading. |
Question : What is the use of friend function ?
Ans :
In object-oriented programming, a friend function, that is a "friend" of a given class, is a function that is given the same access as methods to private and protected data.
A friend function is declared by the class that is granting access, so friend functions are part of the class interface, like methods. Friend functions allow alternative syntax to use objects, for instance f(x) instead of x.f(), or g(x,y) instead of x.g(y). Friend functions have the same implications on encapsulation as methods.
Sometimes a function is best shared among a number of different classes. Such functions can be declared either as member functions of one class or as global functions.
In either case they can be set to be friends of other classes, by using a friend specifier in the class that is admitting them.
Such functions can use all attributes of the class which names them as a friend, as if they were themselves members of that class.
A friend declaration is essentially a prototype for a member function, but instead of requiring an implementation with the name of that class attached by the double colon syntax, a global function or member function of another class provides the match.
Question : What is the functionality of the function strstr and stristr ?
Ans :
Both functions are used to return or finds the first occurence of a substring from a string, and give all string from first occurence to end of string except than stristr() is case-insensitive.
If no match is found then FALSE will be returned.
Example
$email = 'abc@xyz.com’;
$host = strstr($email, '@’);
echo $host;
output: @xyz.com
stristr() does the same thing in Case-insensitive manner
Question : What is the functionality of the function htmlentities ?
Ans :
The htmlentities() function converts characters to HTML entities.
Tip: To convert HTML entities back to characters, use the html_entity_decode() function.
Tip: Use the get_html_translation_table() function to return the translation table used by htmlentities().
Question : How can we get the seconds from the current time, using date function ?
Ans :
Using "s" in date function returns the seconds, with leading zeros.
Question : How can we convert timezones using PHP ?
Ans :
You can use the datetime object or their function aliases for this:
$triggerOn = '04/01/2013 03:08 PM';
$user_tz = 'America/Los_Angeles';
echo $triggerOn; // echoes 04/01/2013 03:08 PM
$schedule_date = new DateTime($triggerOn, new DateTimeZone($user_tz) );
$schedule_date->setTimeZone(new DateTimeZone('UTC'));
$triggerOn = $schedule_date->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
echo $triggerOn; // echoes 2013-04-01 22:08:00
Question : What is meant by urlencode and urldecode ?
Ans :
urlencode(string) — This PHP function is encodes a string to be used in a query part of a URL. URL encoding is used when placing text in a query string to avoid it being confused with the URL itself. It is normally used when the browser sends form data to a web server.
urldecode(string) — This PHP function is decodes the query part of a URL string. URL encoding is used when placing text in a query string to avoid it being confused with the URL itself. It is normally used when the browser sends form data to a web server.
Question : What is difference between functions unlink and unset ?
Ans :
In PHP unlink() is a function for file system handling, unlink() is used to delete files. Suppose you have uploaded a file and wants to delete this file through the coding then unlink() function is used to delete the file.
unset() is a function for variable management. It will make a variable undefined. Or we can say that unset() is used to null out the value of a given variable. OR Unset () is used to destroy a variable in PHP. In can be used to remove a single variable, multiple variables, or an element from an array.
Question : How can we register variables into a session ?
Ans :
There are 3 ways
-
session_start();
$username=$_GET['username'];
session_register('username');
-
session_start();
$username=$_GET['username'];
$HTTP_SESSION_VARS['username']=$username;
-
session_start();
$username=$_GET['username'];
$_SESSION['username']=$username;
Question : How can we get browser properties using PHP ?
Ans :
One can either use Server and execution environment information with $_SERVER OR Look up the browscap.ini file and return the capabilities of the browser.
The following code will return an array of the browser name,version and platform.
echo $_SERVER['HTTP_USER_AGENT'] . "\n\n";
$browser = get_browser();
print_r($browser);
?>
Question : What is the maximum size of the file that can be uploaded using PHP and how can we change this ?
Ans :
By default, the maximum upload file size for PHP scripts is set to 2 megabytes. However, you may want to change these limits. To do this, change the upload_max_filesize and post_max_size directives in your php.ini file.
Note, to ensure that file uploads work correctly, the post_max_size directive should be a little larger than the upload_max_filesize.
After modifying php.ini file(s), you need to restart your HTTP server to use new configuration.
Question : How can we increase execution time of PHP Script ?
Ans :
By changing max_execution_time in php.ini file.
It sets the maximum time in seconds a script is allowed to run before it is terminated by the parser. This helps prevent poorly written scripts from tying up the server. The default setting is 30. When running PHP from the command line the default setting is 0.
If you don't have access to php.ini, you can set it using function ini_set.
For instance, ini_set('max_execution_time', 300); //300 seconds = 5 minutes
Question : Give single line statement that will get value of posted variable when I am not aware of whether its POST variable or GET variable ?
Ans :
$_REQUEST['variablename'] returns the posted value irrespective of POST or GET.
Question : Write down $_SERVER variable elements by which one can fetch
- The browser details of visitor
- The IP Address of visitor
- The currently executing script name
Ans :
- The browser details of visitor - $_SERVER['USER_AGENT']
- The IP Address of visitor - $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']
- The currently executing script name - $_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME']
Question : Which function capitalizes the first letter of each word in a string ?
Question : What is PEAR in PHP ?
Ans :
PEAR is short for "PHP Extension and Application Repository" and is pronounced just like fruit. The purpose of PEAR is to provide
- A structured library of open sourced code for PHP users.
- A system for code distribution and package maintenance.
- A standard style for code written in PHP.
- The PHP Foundation Class (PFC).
- The PHP Extension Community Library (PECL).
- A website, mailing lists and download mirrors to support the PHP / PEAR community.
PEAR is a community driven project with the PEAR Group as the governing body. The project has been founded by Stig S. Bakken in 1999 and quite a lot of people have joined the project since then.
Question : What is MIME ?
Ans :
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is Content-type for a file.
It was designed to allow the formatting of emails so that they can include files easily, and is made up of several parts. In order to be able to instruct email clients what types of files are attached, MIME types were created - short, textual descriptions of the files types that can be recognised by everyone. MIME types are so popular that they are used across the WWW as a whole now, and many operating systems rely on them to decide how to open a file. In emails, attachments are literally copied into the message as an encoded string, with MIME boundary markers being used to tell mail readers where each attachment starts and stops.
Question : What is the functionality of md5 function in PHP ?
Ans :
md5 — Calculates the md5 hash of a string. It Returns the hash as a 32-character hexadecimal number.
Note, It is not recommended to use this function to secure passwords, due to the fast nature of this hashing algorithm.
Question : How can we know the number of days between two given dates using PHP ?
Ans :
$now = time(); // or your date as well
$your_date = strtotime("2010-01-01");
$datediff = $now - $your_date;
echo floor($datediff / (60 * 60 * 24));
OR Using the date_diff() function, you can easily count days between two dates in PHP.
$date1 = date_create("2017-04-15");
$date2 = date_create("2017-05-18");
//difference between two dates
$diff = date_diff($date1,$date2);
//count days
echo 'Days Count - '.$diff->format("%a");
Question : What is the default session time in PHP and how can we change it ?
Ans :
It depends on the server configuration or the relevant directives (session.gc_maxlifetime) in php.ini. Typically the default is 24 minutes (1440 seconds). One can also change through script as ini_set("session.gc_maxlifetime",$intTime);
Question : What types of headers have to add in the mail function in which a file is attached ?
Ans :
$boundary = '–' . md5( uniqid ( rand() ) );
$headers = "From: \"Me\"\n";
$headers .= "MIME-Version: 1.0\n";
$headers .= "Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary=\"$boundary\"";
Question : What is difference between copy() and move() function in PHP File Uploading ?
Ans :
copy: Makes a copy of the file source to dest.
bool copy ( string $source , string $dest [, resource $context ] )
If the destination file already exists, it will be overwritten. If dest is a URL, the copy operation may fail if the wrapper does not support overwriting of existing files. Returns TRUE on success or FALSE on failure.
move: If the file is valid, it was uploaded via PHP's HTTP POST upload mechanism, it will be moved to the filename given by destination. Otherwise no action will occur, and move_uploaded_file() will return FALSE.
bool move_uploaded_file ( string $filename , string $destination )
Question : Describe the importance of DATABASE ABSTRACTION LAYERS in PHP and database connection ?
Ans :
A Database Abstraction Layer (DBAL) is an application programming interface which unifies the communication between a computer application and databases such as SQL Server, DB2, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle or SQLite. Traditionally, all database vendors provide their own interface tailored to their products, which leaves it to the application programmer to implement code for all database interfaces he or she would like to support. Database abstraction layers reduce the amount of work by providing a consistent API to the developer and hide the database specifics behind this interface as much as possible. There exist many abstraction layers with different interfaces in numerous programming languages. If an application has such a layer built in, it is called database-agnostic.
Any abstraction layer will reduce the overall speed more or less depending on the amount of additional code that has to be executed. The more a database layer abstracts from the native database interface and tries to emulate features not present on all database backends, the slower the overall performance. This is especially true for database abstraction layers that try to unify the query language as well like ODBC.

Add new comment